Technical Architecture
This chapter provides an in-depth introduction to Curvine's technical architecture, detailing the functionality, interaction patterns, and design principles of each layer component to help you comprehensively understand how the Curvine system works.
Architecture Overview
Curvine adopts a layered distributed architecture design that ensures clear component responsibilities with excellent scalability and high availability. The entire architecture is primarily divided into three layers: control layer (Master), storage layer (Workers), and access layer (clients: FUSE, SDK, CLI, S3 gateway), which collaborate to complete data storage, processing, and management tasks.
Curvine consists of three main server-side roles plus clients and UFS:
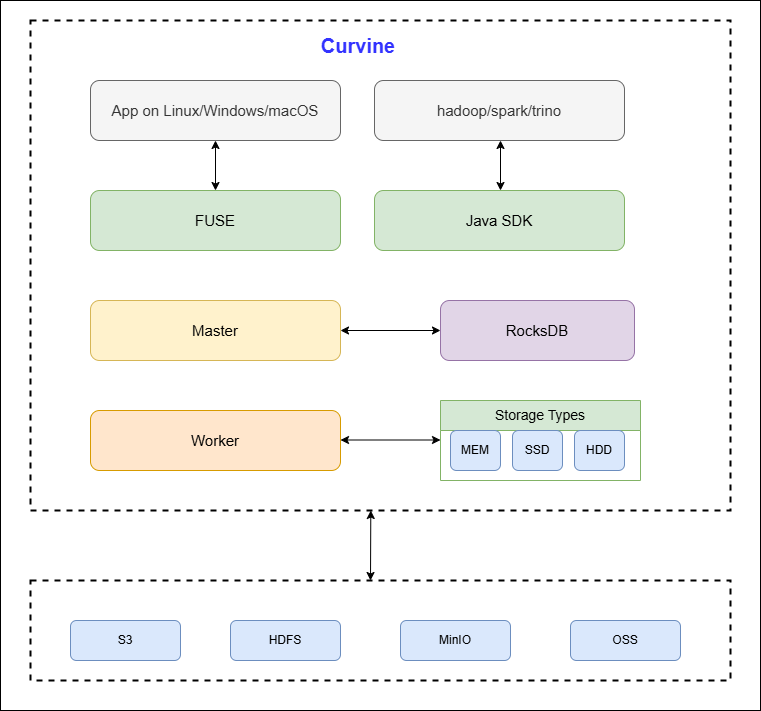
Curvine Client: Data read/write operations are implemented by the client, which calls Curvine server-side interfaces through RPC (metadata from Master, block data from Workers). The client supports multiple access methods:
- FUSE: POSIX-compatible mount, functioning as local storage
- Hadoop Java SDK: Java client for the Hadoop ecosystem
- Rust / Python SDK: Native SDKs for Rust and Python
- S3 gateway: S3-compatible object API
- CLI (
cv): Command-line management, mount, fs operations, load, report, node
Master: The core control node; responsible for metadata (directory tree, file inodes, block locations), Worker registration, block allocation, and UFS mount table. Master can run as multiple nodes forming a Raft group for high availability; only the Raft leader serves metadata writes.
Worker: Stores block data and serves block read/write RPC; reports to Master via heartbeat. Does not hold file system metadata.
UFS: Underlying storage (S3, HDFS, etc.) accessed through Curvine’s data orchestration; Curvine provides a unified file system view over mounted UFS paths and native paths.
For deployment topology and component roles, see Deployment Architecture. For internal data flow (journal, replay, client read/write), see Basic Architecture.
High-Performance Design
To achieve high performance, high concurrency, and low resource consumption, Curvine adopts the following technologies and design principles:
- Pure Rust Implementation: Curvine is implemented entirely in Rust, avoiding performance bottlenecks and resource consumption of traditional languages while ensuring code safety and stability
- High-Performance RPC Framework: Curvine implements a custom RPC communication framework supporting efficient data transmission with asynchronous I/O and zero-copy implementation within the framework
- Zero-Cost Abstractions: Zero-cost abstraction design where core modules directly interface with underlying systems, avoiding unnecessary abstraction layers and improving system performance and resource utilization
- Asynchronous I/O: Asynchronous I/O design fully utilizes system resources, avoiding blocking waits and improving system concurrent processing capabilities
- Zero-Copy: Zero-copy design avoids data copying and memory allocation, reducing system memory usage and resource consumption
High Availability Design
Curvine adopts distributed architecture design with multi-replica mechanisms and failover mechanisms to ensure system high availability:
- Raft Protocol: Uses Raft protocol to implement distributed consistency, ensuring data consistency and reliability
- Automatic Failover: Automatic failover mechanism that switches to backup nodes when primary nodes fail, ensuring system high availability
- Multi-Replica Mechanism: Multi-replica mechanism ensures data redundancy backup, improving system reliability and fault tolerance
- Snapshot Mechanism: Lightweight snapshot mechanism for periodic data backup, improving system recovery speed and stability